Sanskrit Glossary
A)
Abharana: adornment; vastabharana is adornment with clothes
Abhyasa: exercise, practice
Acarya: teacher; literally ‘one who walks with’
Advaita: concept of non-duality; that individual self and the cosmic SELF are one and the same; as different from the concepts of dvaita and visistadvaita, which consider self and SELF to be mutually exclusive
Ahara: food; also with reference to sensory inputs as in pratyahara
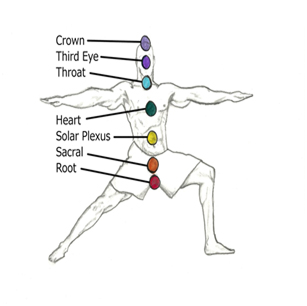
Ajna: order, command; the third eye energy centre
Akasa: space, sky; subtlest form of energy of universe
Amrta, amrt: divine nectar whose consumption leads to immortality
Anahata: that which is not created; heart energy centre
Ananda: bliss; very often used to refer to joy, happiness etc
Angulimaal: a Highway robber and murderer who wore a garland with the fingers of his victims. He was later transformed by Buddha and became a monk in Buddha’s monastery
Anjana: collyrium, black pigment used to paint the eye lashes
Annamalai Swamigal: enlightened disciple and personal assistant of enlightened master Bhagavan Ramana Maharshi
Apas: water
Aarti: Worship of the deity using lit lamps
Arti: Worshipping with a flame or light, as with a lamp wiht oiled wick, or burning camphor
Ashtavakra: An enlightened sage of ancient India, authorised Ashtavakra Samhita
Asirvad: blessing
Ashtanga Yoga: Eight fold path to enlightenment prescribed by Patanjali in his Yoga Sutra
Asraya: Grounded in reality; asraya dosa, defect related to reality
Atma, atman: individual Self; part of the universal Brahman
Atma Shatakam: Poem of six stanzas composed by enlightened master Adi Shankara, summarizing the concept ofadvaita or non-dualistic philosophy
Aurangazeb: One of the last Mughal emperorsgreatest of all the Mughal emperors who ruled India; a despotic ruler
B)
Beedi: Local Indian cigarrette
Bija: seed; bija-mantra refers to the single syllable mantras used to invoke certain deities, e.g., gam for Ganesha
Bhagavan: literally god; often used for an enlightened Master
Bhavana: visualization
Brahma: The God of creation in the Hindu Trinity of Brahma (Creator), Visnu (Preserver) and Siva (Rejuvinator)
Bhakti: devotion; bhakta, a devotee
Bhagavatam: Devotional stories on Lord Krishna, compiled by Veda Vyasa
C)
Chakra: Literally a ‘wheel’; refers to energy centers in the mind body system
Chaksu: Intelligent power behind senses.
Chandala: An untouchable; usually one who skins animals
Chandana: sandalwood
Chitta: Mind; also manas, buddhi
D)
Dakshinayana: Sun’s movement South starting 21st July
Darshan: That which is seen; usualy referred to seeing Divinity
Dharma: Righteousness
Dhee: Wisdom
Diksha, Deeksha: Grace bestowed by the Master and the energy transferred by Master on disciple at initiation or any other time; may be through a mantra, a touch, a glance or even a thought.
Dosha: Defect
Dhyana: Meditation
Drishti: That which is seen
G)
Gada, Gadha: Weapon, similar to a mace; also Gadhayudha
Gopi, Gopika: Literally a cowherd; usually referred to the devotees, men and women, who played with Krishna, and were lost in Him
Gopura, gopuram: Temple tower
Grihasta: A householder; a married person; from the word griha meaning house
Guna: the three human behavioral characteristics or predipositions; satva, rajas and tamas
Guru: Master; literally one who leads from gu darkness to ru light
Gurukul: literally ‘tradition of guru’, refers to the ancient education system in which children were handed over to aguru at a very young age by parents for upbringing and education.
H)
Homa: Ritual to Agni, the God of fire; metaphorically represents the transfer of energy from the energy of Akasa (space) , through Vayu (Air), Agni (Fire), Apu (Water), and Prithvi (Earth) to humans.
I)
Iccha: Desire
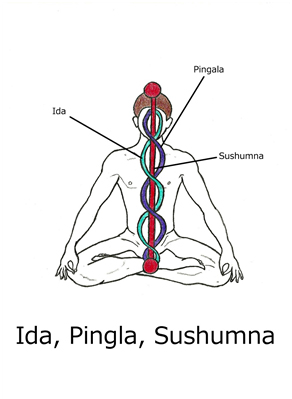
Ida: along with pingala and sushumna the virtual energy pathways through which pranic energy flows.
Ithihasa: Legend, epic, mythological stories
J)
Jaati: Birth; jaati dosha, defect related to birth
Jagrat: awake
Japa: Literally ‘muttering’; conitinuous repetition of the name of divinity
Jiva samadhi: Burial place of an aenlighetend master, where his spirit lives on; jiva means living.
Jyotisha: Astrology; jyotish is an astrologer
K)
Kaivalya: Liberation; same as moksha, nirvana ..
Kala: Time
Kalpa: Vast period of time; similar to Yuga.
Kalpana: Imagination
Karma: spiritual law of cause and effect, driven by vasana and samskara
Kosha: Energy layer surrounding body; there are 5 such layers. These are: annamaya or body, pranamaya or breath, manonmaya or thoughts, vigyanamaya or sleep and anandamaya or bliss koshas.
Kriya: Action
Kshana: Moment in time; refers to time between two thoughts
Kshatriya: Caste or varna group of warriors.
Kundalini: Ebergy that resides at the root chakra ‘muladhara’
M)
Maha: Great; as in maharishi, great sage; mahavakya, great scriptural saying
Mala: a garland, a necklace; rudraksha mala is a necklace made of the seeds of the rudraksha tree.
Manan: What is thought
Manas: Mind; also buddhi, chitta.
Mandir: Temple
Mangal: auspicious; mangal sutra, literally auspicious thread, the yellow or gold thread or necklace a married Hindu woman wears
Mantra: A sound, a formula; sometimes a word or a set of words, which because of their inherent sound , have energizing properties. Mantras are used as sacred chants to worship the Divine; Mantra, tantra and yantra are approaches in spiritual evolution.
Maya: That which is not; not reality ; illusion; all life is maya according to advaita.
Moksha: liberation; same as nirvana, samadhi, turiya etc.
Muladhara: the first energy center, mula is root, adhara is foundation, here existence
N)
Nadi: River
Naadi: Nerve; also an energy pathway which is not physical
Naga: a snake; a naga sadhu is an ascetic belonging to a group that wears no clothes.
Namaskar: Traditional greeting with raised hands palms closed
Nanda: unbound
Nari: woman
Nidhityasan: What is expressed
Nimitta: Reason; nimitta dosha, defect based on reason
Nirvana: liberation ; ‘nibbhana’ in Pali language; same as moksha, samadhi.
Niyama: The second of eight paths of Patanjali’s Ashtanga Yoga; refers to a number of day to day rules of observance for a spiritual path.
P)
Papa: sin
Phala: Fruit; phalasruti refers to result of worship
Paramahamsa: Literally the ‘supreme swan’; refers to an enlightened being of a specific level.
Parikrama: The ritual of going around a holy location, such as a hill or water spot
Parivrajaka: Wandering by an ascetic monk
Pingala: please see Ida
Prana: Life energy; also refers to breath; pranayama is the control of breath
Pratyahara: Literally ‘staying away from food’; in this case refers to control of alls senses as part of the eight foldashtanga yoga.
Prithvi: Earth energy
Purohit: Priest
Puja: normally any worship, but often referred to a ritualistic worship
Punya: merit
Purana: Epics and mythological stories such as Mahabharata, Ramayana etc.
Purna: Literally ‘complete’; refers in the advaita context to Reality.
R)
Rajas, rajasic: the mid characteristic of the three human guna or behavior mode, referring to aggressive action.
Putra: son; putri is daughter.
Rakta: blood
Ratri: Intensity; also night;
Rishi: A spiritual sage
S)
Sadhana: Practice, usually a spiritual practice
Sadhu: literally a ‘good person’; refers to an ascetic; same as sanyasi
Sahasranama: Thousand names of God; available for many Gods and Goddesses, which devotees recite
Sahasrara: thousand petal lotus, the crown energy center
Sakti: Energy; intelligent energy; Parasakti refers to Universal Energy; Divinity; considered feminine; masculine aspect of Parasakti is the Purusha.
Samadhi: state of no mind, no thoughts; adhi is original and sama is becoming that; literally, becoming one’s original state; liberated, enlightened state. Three levels of samadhi are referred to sahaja, which is transient, savikalpa, in which the person is no longer capable of normal activities, and nirvikalpa, where the liberated person performs activities as before.
Samsaya: Doubt
Samskara: embedded memories of unfulfilled desires stored in the unconscious that drive us into decisions, intokarmic action.
Samyama: Complete concentration
Sankalpa: Decision
Sanyas: Giving up worldly life; sanyasi or sanyasin, a monk, an ascetic; sanyasini, as referred to a lady monk.
Sastra: Sacred texts
Satva, satvic: the highest guna of spiritual calmness
Siddhi: Extraordinary powers attained through spiritual practice
Sishya: Disciple
Simha: Lion; Simha Swapna is nightmare.
Siva: Rejuvenator in the Trinity; often spelt as Shiva. Siva also means ‘Causeless Auspiciousness’; in this sense, Sivaratri, the day when Siva is worshipped is that moment when the power of this Causeless Auspiciousness is intense.
Smarana: Remembrance; constantly remembering the Divine.
Smruti: Literally ‘that which is remembered’; refers to later day Hindu works which are rules, regulations, laws and epics, such as Manu’s works, Puranas etc.
Sradha: sincere
Sravan: what is heard
Srishti: That which is, which is created
Sruti: Literally ‘that which is heard’; refers to the ancient scriptures of Veda, Upanishad and Bhagavad Gita, considered to be Words of God
Stotra: Devotional verses, to be recited or sung
Sudra: Caste or varna group of manual laborers.
Sutra: Literally ‘thread’; refers to epigrams, short verses which impart spiritual techniques.
Sunya: Literally zero; however, Buddha uses this word to mean Reality
Sushumna: Please see Ida
Swadishthana: where Self is established; the groin or spleen energy center
Swapna: Dream
Swatantra: Freedom
T)
Tamas, tamasic: the lowest guna of laziness or inaction
Tantra: Esoteric Hindu techniques used in spiritual evolution
Tapas: Severe spiritual endeavor, penance
Thatagata: Buddhahood, suchness..a pali word
Tirta: Water; tirtam is a holy river spot and a pilgrimage center
Trikala: All three time zones, past, present and future; trikalajnani is one who can see all three at the same time; an enlightened v=being beyond time and space.
Turiya: state of samadhi, no mind
U)
Upanishad: Literally ‘sitting below alongside’ referring to a disciple learning from the Master; refers to the ancient Hindu scriptures which along with the Veda , form sruti.
Uttarayana: Sun’s movement North, starting 21st January
V)
Vaisya: Caste or varna group of tradesmen.
Vanaprastha: The third stage in one’s life, when a householder, man or woman, gives up wordly activities and focuses on spiritual goals
Varna: Literally color; refers to the caste grouping in the traditional Hindu social system; originally based on aptitude, and later corrupted to privilege of birth.
Vasana: the subtle essence of memories and desires, samskara, that get carried forward from birth to birth
Vastra: Clothes;
Vastraharana; removal of clothes, often used to refer to Draupadi’s predicament in Mahabharata, when she is forcibly undressed by the Kaurava Prince.
Vayu: Air
Veda: Literally knowledge; refers to ancient Hindu scriptures, believed to have been received by enlightened rishi at the being level; also called sruti, along with Upanishad.
Vibhuti: sacred ash worn by many Hindus on forehead; said to remind themselves of the transient nature of life; also glories.
Vidhi: literally law, natural law; interpreted as fate or destiny
Vidhya: knowledge
Vishada: Depression, dilemma etc
Vishnu: Preserver in the Trinity; His incarnations include Krishna, Rama etc.; also means ‘all encompassing’
Vishwarupa: Universal Form
Y)
Yama: discipline as well as death; One of the eight fold paths prescribed in Patanjali’s Ashtanga Yoga; refers to spiritual regulations of Satya (Truth). Ahimsa (Non Violence), Aparigraha (Living simply); Asteya (Not coveting other’s properties) and Brahmacharya (giving up fantasies); Yama is also the name of the Hindi God of Justice and Death.
Yantra: Literally ‘tool’; usually a mystical and powerful graphic diagram, such as the Sri Chakra, inscribed on a copper plate, and sanctified in a ritual blessed by a Divine presence or an Enlightened Master
Yoga: literally union, union of the individual self and the divine Self; often taken to mean Hatha Yoga, which is one of the components relating to specific body postures.
Yuga: a long period of time as defined in Hindu scriptures; there are four yugas: Satya, Treta, Dwapara and Kali